Input-Output Models
Types of Models
Open Model: Some production consumed internally by industries, the rest is consumed by external bodies.
Closed Model: All of the production is consumed by industries
Input-Output Matrix
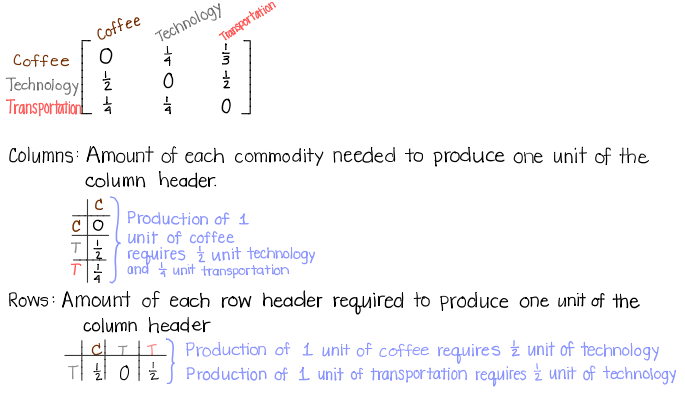
An input-output matrix describes the amount of each commodity used in the production of one unit of each commodity.
Example: Suppose an economy involves coffee, technology, and transportation.
Production of 1 unit of coffee requires 1/2 unit of technology and 1/4 unit of transportation.
Production of 1 unit of technology requires 1/4 unit of coffee and 1/4 unit of transportation.
Production of 1 unit of transportation requires 1/3 unit of coffee and 1/2 unit of technology.
Then our input-output matrix, A, will be:
Production Matrices
The Production Matrix gives the amount of each commodity produced.
Example:
Let's say we want to produce 60 units of coffee, 52 units of technology, and 48 units of transportation.
Then our production matrix will be:
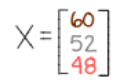
Demand Matrices
So far, we have two matrices:
- We have our input-output matrix, A, which represents the number of units of each commodity used to produce 1 unit of each of the commodities.
- We also have our production matrix, X, which represents the number of units of each commodity produced.