L8.3 - Sample Spaces
Learning Intentions and Success Criteria
- Create and coordinate different representations for recording sample space for chance experiments
- Use organized lists, tables, and tree diagrams to calculate probabilities for compound events
- Create organized lists, tables, and tree diagrams and use them to calculate probabilities
3.1: Rolling Cubes
When rolling two standard number cubes, one of the possible outcomes is 1 and 1. 1. What are the other possible outcomes?
2. How many outcomes are in the sample space?
3.2: Spinner Sample Space
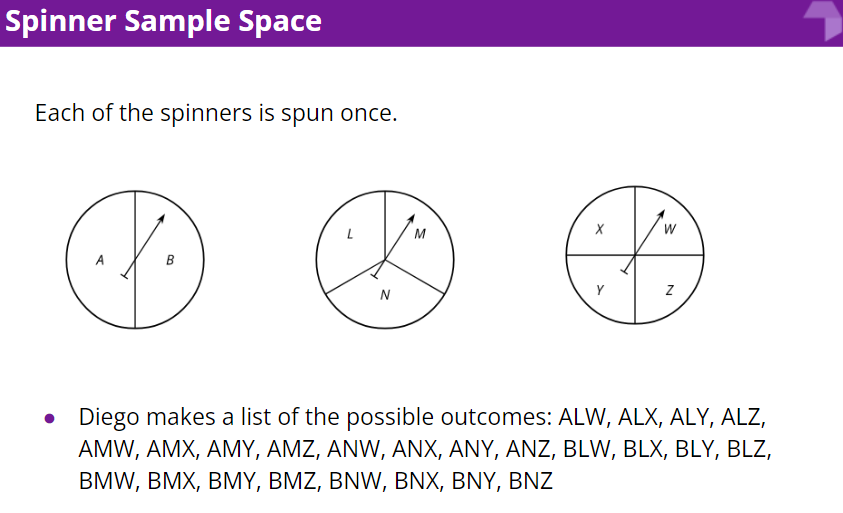

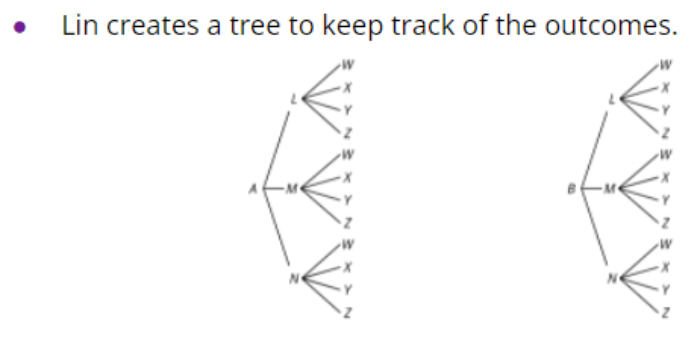
1. How many outcomes are in the sample space for this experiment?
2. One of the outcomes from Diego’s list is BLX. Where does this show up in Tyler's method? Where is it in Lin’s method?
3. When spinning all three spinners, what is the probability that:
4. If a fourth spinner that has 2 equal sections labeled S and T is added, how would each of the methods need to adjust?
3.3: Sample Space Practice
List all the possible outcomes for each experiment. 1. A standard number cube is rolled, then a coin is flipped.
2. Four coins are flipped.
3. The two spinners are spun.

3. The two spinners are spun.
4. A class block is chosen from 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, then a subject is chosen from English or math.




Learning Intentions and Success Criteria
- Create and coordinate different representations for recording sample space for chance experiments
- Use organized lists, tables, and tree diagrams to calculate probabilities for compound events
- Create organized lists, tables, and tree diagrams and use them to calculate probabilities
Cool-Down: Sample Space of Sample Space
One letter is chosen at random from the word SAMPLE then a letter is chosen at random from the word SPACE. 1. Write all of the outcomes in the sample space of this chance experiment.
2. How many outcomes are in the sample space?
3. What is the probability that the letters chosen are AA? Explain your reasoning.

